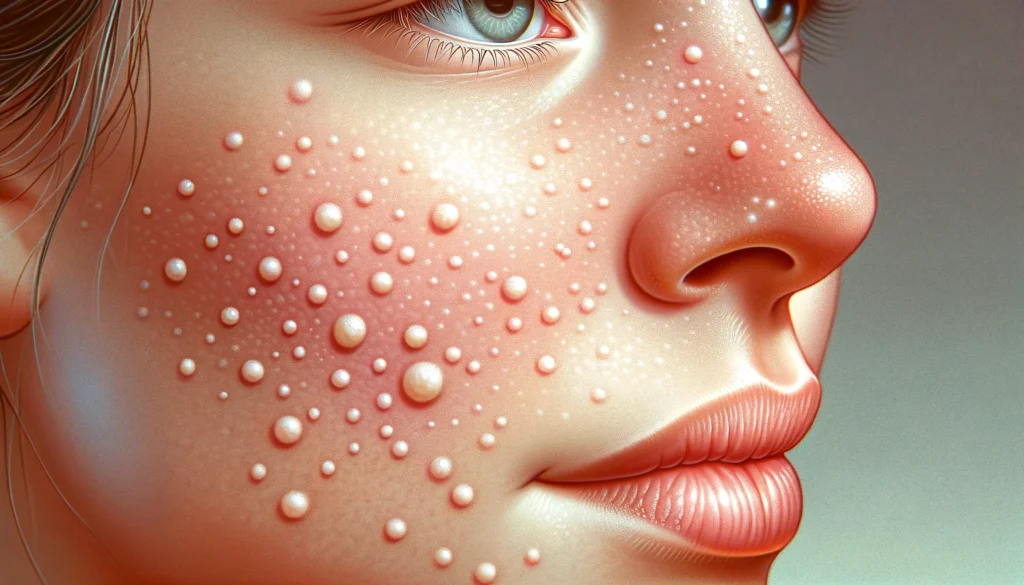
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on understanding milia, those tiny white bumps that often appear on the skin. In this article, we will delve into the causes behind milia formation and explore various treatment options available to address this concern. Whether you’re dealing with milia yourself or simply curious about this skin condition, read on to gain valuable insights and practical solutions.
What Are Milia?
Milia, also known as milk spots, are small, white cysts that typically develop on the face, cheeks, nose, and around the eyes. These cysts form when keratin becomes trapped beneath the surface of the skin, leading to tiny, raised bumps. While milia are harmless and painless, they can be a cosmetic nuisance for many individuals.
Understanding Milia Formation
Milia form when dead skin cells become trapped in pockets beneath the skin’s surface. Unlike acne, which is caused by excess oil and bacteria clogging pores, milia occurs when keratin (a protein found in the outer layer of the skin) becomes trapped, leading to the formation of small cysts.
Types of Milia
There are several types of milia, including primary milia, which develop spontaneously, and secondary milia, which arise due to skin damage or trauma. Neonatal milia, commonly seen in newborns, and milia en plaque, which occur in clusters, are also observed.
Causes of Milia
Understanding the underlying causes of milia is crucial for effective management. While the exact cause may vary depending on the type of milia, several factors contribute to their development.
Excessive Sun Exposure
Prolonged exposure to the sun’s harmful UV rays can damage the skin and lead to the formation of milia. UV radiation can thicken the outer layer of the skin, making it more difficult for dead skin cells to shed naturally.
Skincare Products
Certain skincare products, such as heavy creams or lotions, can potentially clog pores and contribute to the development of milia. These products may contain ingredients that are too rich or occlusive for the skin, leading to trapped keratin and the formation of cysts.
Trauma to the Skin
In some cases, trauma or injury to the skin, such as burns or rashes, can trigger the formation of secondary milia. The skin’s healing process may result in the accumulation of keratin, causing small cysts to develop.
Genetic Factors
Genetics may also play a role in predisposing individuals to milia. Some people may inherit a tendency to develop milia due to genetic factors that affect skin cell turnover and keratin production.
Treatment Options for Milia
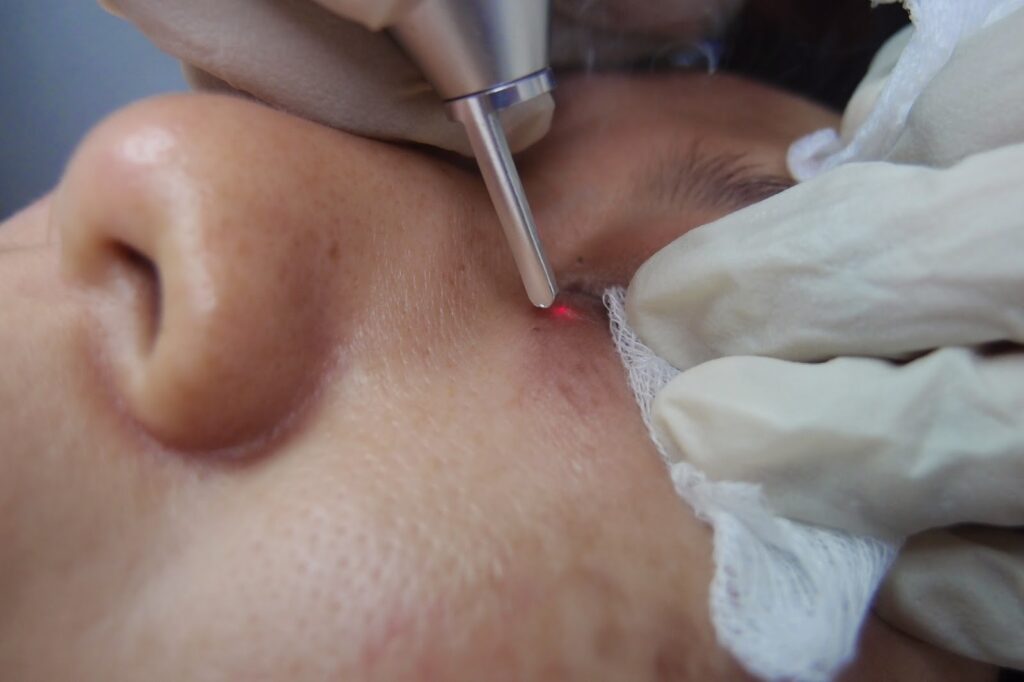
While milia often resolve on their own over time, certain treatment options can help expedite the process and prevent new cysts from forming.
Gentle Exfoliation
Regular exfoliation can help remove dead skin cells and prevent the buildup of keratin that leads to milia. Opt for gentle exfoliants containing ingredients like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) to promote cell turnover.
Topical Retinoids
Retinoids, derivatives of vitamin A, can help promote cell turnover and prevent the formation of new milia. Over-the-counter retinol creams or prescription-strength retinoids can be effective in treating milia.
Professional Extraction
For stubborn or persistent milia, a dermatologist may perform a procedure known as “lancing” or “extraction” to remove the cysts safely. This involves using a sterile needle or blade to carefully extract the contents of the cyst without causing damage to the surrounding skin.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels containing ingredients like salicylic acid or glycolic acid can help exfoliate the skin and improve its texture. Regular peels can help reduce the appearance of milia and prevent new cysts from forming.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: Can milia be prevented?
A: While milia cannot always be prevented, practicing good skincare habits such as regular exfoliation and avoiding heavy, pore-clogging products can help reduce the likelihood of their occurrence.
Q: Are milia contagious?
A: No, milia are not contagious. They are benign cysts that develop within the skin and are not caused by bacteria or viruses.
Q: Can I pop or squeeze Milia?
A: It is not recommended to pop or squeeze milia at home, as this can lead to skin damage and potential scarring. Leave extraction to trained professionals such as dermatologists.
Q: Are there any home remedies for treating milia?
A: While home remedies such as applying warm compresses or using certain natural oils may help soften milia, they may not always be effective in resolving the cysts completely. Consult with a dermatologist for personalized treatment recommendations.
Q: Can Milia go away on their own?
A: In many cases, milia will resolve on their own over time without any treatment. However, certain interventions may help speed up the process and prevent new cysts from forming.
Q: Are there any dietary factors that can contribute to milia?
A: While specific dietary factors have not been conclusively linked to milia, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can promote overall skin health and may indirectly help prevent milia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the causes and treatment options for milia is essential for effectively managing this common skin condition. By implementing gentle skincare practices, seeking professional guidance when necessary, and adopting a proactive approach to skin health, individuals can successfully address milia and achieve clear, radiant skin.
